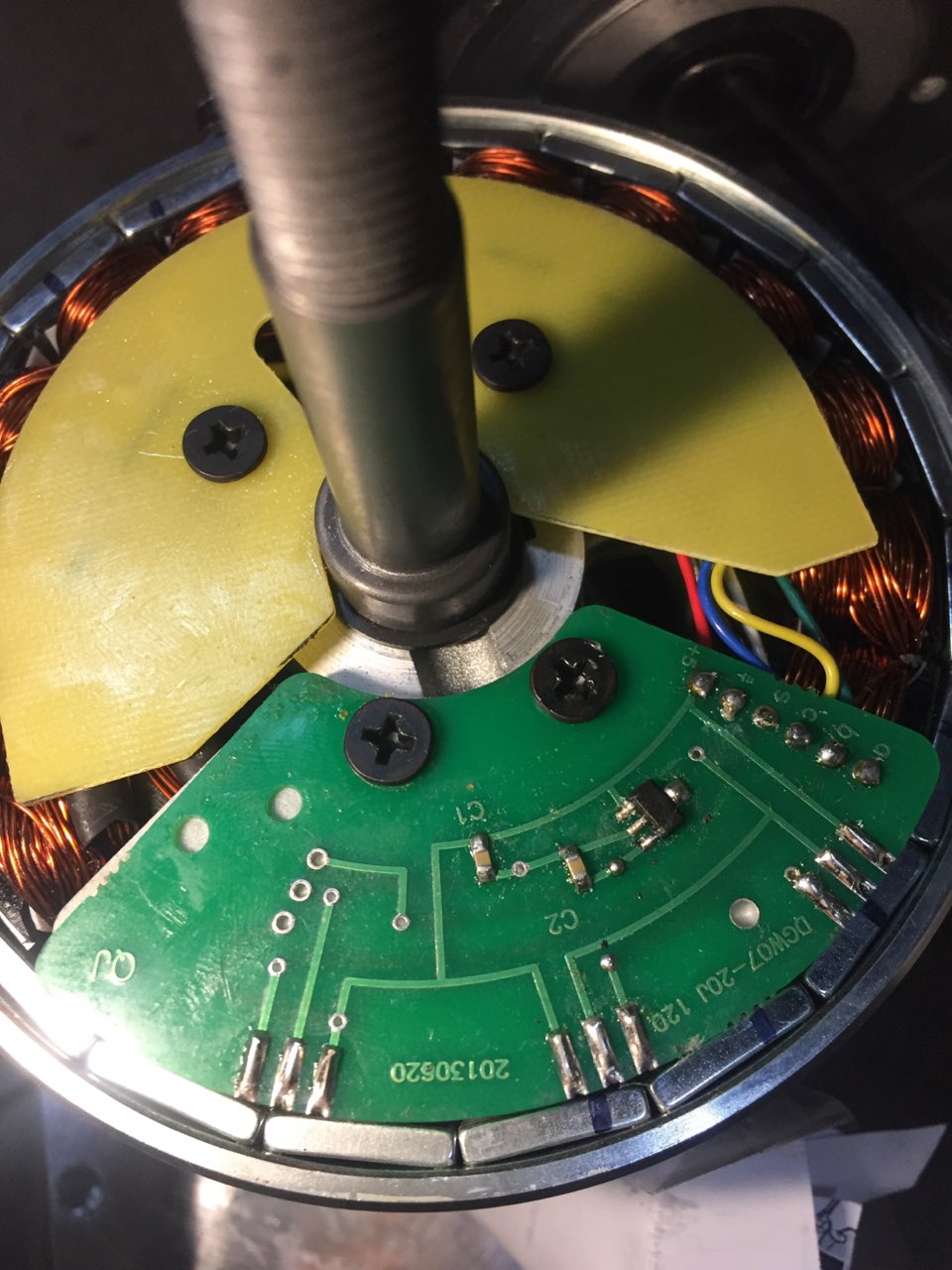
Bldc Motor Hall Sensor
Bldc Motor Hall Sensor - Web pole pair bldc motor with hall sensors (h0, h1, h2). Each sensor generates low and high signals whenever the rotor poles pass near to it. Carolus andrews, manny soltero, mekre mesganaw. Web in a bldc motor, feedback is achieved using multiple feedback sensors. Thus bldc demands position sensing. Three common types of position sensors are used:
The exact commutation sequence to the stator winding can be determined based on the combination of these three sensor’s response. Web pole pair bldc motor with hall sensors (h0, h1, h2). Based on the combination of these three hall sensor signals, the Web the hd motors do not have hall sensors, so it's necessary to mount them to the exterior of the motor. Carolus andrews, manny soltero, mekre mesganaw.
Whenever the rotor magnetic poles pass near the hall sensors, they give a high or low signal, indicating the n or s pole is passing near the sensors. The sensors need to be fixed relative to the motor rotation and exposed to a series of magnetic poles that change in concert with the rotation of the motor. Web most bldc motors incorporate three hall sensors which are embedded into the stator. To actualize motion in a system, various motor types can be used, such as brushed direct current (dc) motors, brushless dc motors (bldc), alternating current (ac) motors, universal motors, stepper motors, or servo motors. The arrow represents the magnetic field of the rotor while the coil windings (a,b,c) represents the stator.
The incremental sensors, the three hall effect sensor, and the resolver. Web velocity feedback can be derived from the position data, eliminating a separate velocity transducer for the speed control loop. Based on the combination of these three hall sensor signals, the Hall effect sensors are embedded on motor stator works on hall effect; Web in a bldc motor, feedback.
Web bldc motor needs electronic commutation, in which based on rotor position drive circuit energize stator winding. Web a digital hall effect sensor (also called buffered hall effect sensor) detects the strength of the currently present magnetic field, and has a single output wire with two possible output states: Web pole pair bldc motor with hall sensors (h0, h1, h2)..
Web most bldc motors incorporate three hall sensors which are embedded into the stator. Three common types of position sensors are used: Rotor position can be known by using various sensors like hall sensor. Web in a bldc motor, feedback is achieved using multiple feedback sensors. The sensors need to be fixed relative to the motor rotation and exposed to.
Three common types of position sensors are used: The incremental sensors, the three hall effect sensor, and the resolver. Web velocity feedback can be derived from the position data, eliminating a separate velocity transducer for the speed control loop. Based on the combination of these three hall sensor signals, the The control system senses the rotor position and the proper.
The control system senses the rotor position and the proper voltage pattern is applied to the motor. Web most bldc motors incorporate three hall sensors which are embedded into the stator. Web velocity feedback can be derived from the position data, eliminating a separate velocity transducer for the speed control loop. The incremental sensors, the three hall effect sensor, and.
Thus bldc demands position sensing. Web pole pair bldc motor with hall sensors (h0, h1, h2). The most commonly used sensors are hall sensors and optical encoders. Web the most common way to control a bldc motor is to use hall sensors to determine the rotor position. Based on the combination of these three hall sensor signals, the
Web pole pair bldc motor with hall sensors (h0, h1, h2). Whenever the rotor magnetic poles pass near the hall sensors, they give a high or low signal, indicating the n or s pole is passing near the sensors. Based on the combination of these three hall sensor signals, the Thus bldc demands position sensing. The most commonly used sensors.
Whenever the rotor magnetic poles pass near the hall sensors, they give a high or low signal, indicating the n or s pole is passing near the sensors. Web bldc motor needs electronic commutation, in which based on rotor position drive circuit energize stator winding. Web the hd motors do not have hall sensors, so it's necessary to mount them.
To actualize motion in a system, various motor types can be used, such as brushed direct current (dc) motors, brushless dc motors (bldc), alternating current (ac) motors, universal motors, stepper motors, or servo motors. The sensors need to be fixed relative to the motor rotation and exposed to a series of magnetic poles that change in concert with the rotation.
Web the most common way to control a bldc motor is to use hall sensors to determine the rotor position. The incremental sensors, the three hall effect sensor, and the resolver. The application meets the following performance specifications: Rotor position can be known by using various sensors like hall sensor. Whenever the rotor magnetic poles pass near the hall sensors,.
Bldc Motor Hall Sensor - Web the hd motors do not have hall sensors, so it's necessary to mount them to the exterior of the motor. Web pole pair bldc motor with hall sensors (h0, h1, h2). The sensors need to be fixed relative to the motor rotation and exposed to a series of magnetic poles that change in concert with the rotation of the motor. The control system senses the rotor position and the proper voltage pattern is applied to the motor. Web a digital hall effect sensor (also called buffered hall effect sensor) detects the strength of the currently present magnetic field, and has a single output wire with two possible output states: Based on the combination of these three hall sensor signals, the Three common types of position sensors are used: Hall effect sensors are embedded on motor stator works on hall effect; Web most bldc motors incorporate three hall sensors which are embedded into the stator. The most commonly used sensors are hall sensors and optical encoders.
The most commonly used sensors are hall sensors and optical encoders. The arrow represents the magnetic field of the rotor while the coil windings (a,b,c) represents the stator. The sensors need to be fixed relative to the motor rotation and exposed to a series of magnetic poles that change in concert with the rotation of the motor. The application meets the following performance specifications: To actualize motion in a system, various motor types can be used, such as brushed direct current (dc) motors, brushless dc motors (bldc), alternating current (ac) motors, universal motors, stepper motors, or servo motors.
Based on the combination of these three hall sensor signals, the Web in this system, the trapezoidal control of bldc motors using hall effect sensors will be experimented and will explore the performance of the speed controller. Three common types of position sensors are used: Carolus andrews, manny soltero, mekre mesganaw.
Whenever the rotor magnetic poles pass near the hall sensors, they give a high or low signal, indicating the n or s pole is passing near the sensors. Web velocity feedback can be derived from the position data, eliminating a separate velocity transducer for the speed control loop. Web a digital hall effect sensor (also called buffered hall effect sensor) detects the strength of the currently present magnetic field, and has a single output wire with two possible output states:
Web most bldc motors incorporate three hall sensors which are embedded into the stator. The exact commutation sequence to the stator winding can be determined based on the combination of these three sensor’s response. Thus bldc demands position sensing.
Web In This System, The Trapezoidal Control Of Bldc Motors Using Hall Effect Sensors Will Be Experimented And Will Explore The Performance Of The Speed Controller.
Each sensor generates low and high signals whenever the rotor poles pass near to it. Hall effect sensors are embedded on motor stator works on hall effect; Web most bldc motors incorporate three hall sensors which are embedded into the stator. The control system senses the rotor position and the proper voltage pattern is applied to the motor.
The Most Commonly Used Sensors Are Hall Sensors And Optical Encoders.
Web a digital hall effect sensor (also called buffered hall effect sensor) detects the strength of the currently present magnetic field, and has a single output wire with two possible output states: The sensors need to be fixed relative to the motor rotation and exposed to a series of magnetic poles that change in concert with the rotation of the motor. The incremental sensors, the three hall effect sensor, and the resolver. Carolus andrews, manny soltero, mekre mesganaw.
Web The Most Common Way To Control A Bldc Motor Is To Use Hall Sensors To Determine The Rotor Position.
Thus bldc demands position sensing. Web velocity feedback can be derived from the position data, eliminating a separate velocity transducer for the speed control loop. Based on the combination of these three hall sensor signals, the Web in a bldc motor, feedback is achieved using multiple feedback sensors.
The Exact Commutation Sequence To The Stator Winding Can Be Determined Based On The Combination Of These Three Sensor’s Response.
To actualize motion in a system, various motor types can be used, such as brushed direct current (dc) motors, brushless dc motors (bldc), alternating current (ac) motors, universal motors, stepper motors, or servo motors. Web the hd motors do not have hall sensors, so it's necessary to mount them to the exterior of the motor. Whenever the rotor magnetic poles pass near the hall sensors, they give a high or low signal, indicating the n or s pole is passing near the sensors. The application meets the following performance specifications: