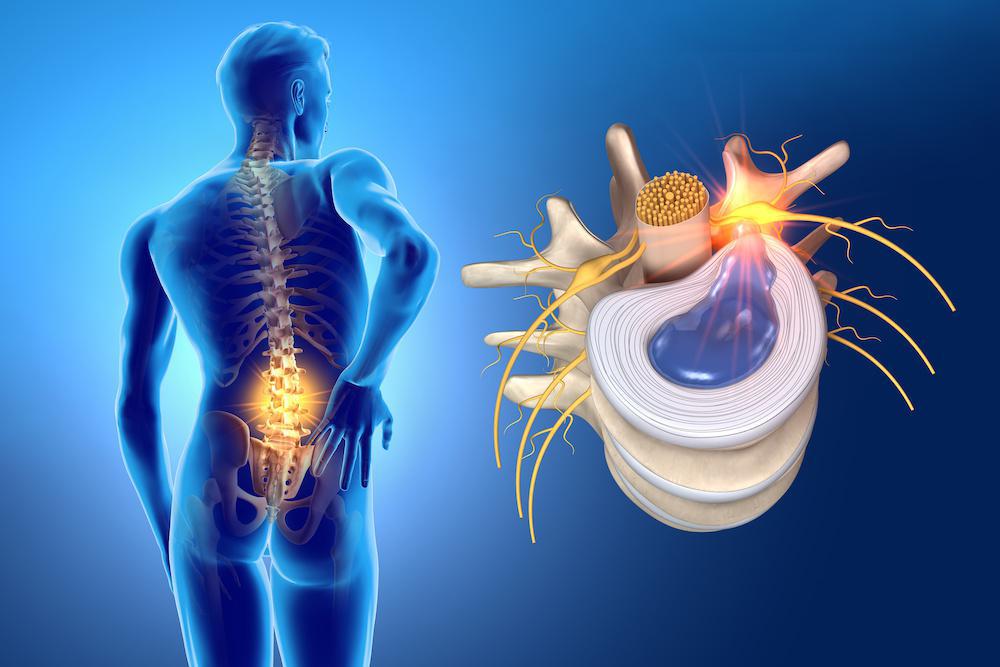
Disc Herniation Size Chart
Disc Herniation Size Chart - The total canal area, and the area of the disc herniation. What causes lumbar disk disease? As a visual picture, the disc looks like a cream filled donut without a hole. Web a spinal disk has a soft, jellylike center called a nucleus. Anatomy and function of the spine. Patients who did not receive surgery had an average herniation size that occupied 31.2% of the canal, whereas patients who received surgery had disc herniations that occupied 31.5% of the canal on average.
Web this series was used to develop the msu classification as an objective measure of lumbar disc herniation on mri to define “substantial”. Web a “disc herniation” is defined as a discal prominence that does not exceed 50% of the disc circumference. The treatment procedure and recovery time depend on the stage of the slipped disc. In rare cases a large disc herniation can lead to cauda equina syndrome which requires emergent diagnosis and treatment. Web a lumbar disc herniation is a change in a spinal disc in the lower back, caused by degeneration or injury.
Please review the document entitled: Review the evaluation of cervical disc herniations. The intervertebral discs are the cushions that act as shock absorbers between each of the vertebra in your spine. A herniated disk is sometimes called a slipped disk or a ruptured disk. A herniated disk occurs when some of the nucleus pushes out through a tear in the annulus.
Web to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of limited discectomy (ld) and aggressive discectomy (ad) performed via spinal endoscopy using the transforaminal approach in patients with lumbar disc herniation(ldh) we conducted a retrospective review of patients who underwent percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal. Outline the treatment and management options available for cervical disc herniations. A slipped intervertebral disc passes through four.
A herniation may contain nucleus pulposus, vertebral endplate cartilage, apophyseal bone/ osteophyte and annulus fibrosus. For comparison purposes, please refer to figure 1. In rare cases a large disc herniation can lead to cauda equina syndrome which requires emergent diagnosis and treatment. Web disc herniation are most of the time asymptomatic and 75% of the intervertebral disc herniation recover spontaneously.
A slipped intervertebral disc passes through four stages. The nucleus is encased in a tougher, rubbery exterior, known as the annulus. Web a herniated disc (also called bulged, slipped or ruptured) is a fragment of the disc nucleus that is pushed out of the annulus, into the spinal canal through a tear or rupture in the annulus. Outline the treatment.
Web a spinal disk has a soft, jellylike center called a nucleus. The dotted line represents the margin of the underlying vertebral endplate. What causes lumbar disk disease? The total canal area, and the area of the disc herniation. Learn more about the options for treatment.
Web a “disc herniation” is defined as a discal prominence that does not exceed 50% of the disc circumference. Patients who did not receive surgery had an average herniation size that occupied 31.2% of the canal, whereas patients who received surgery had disc herniations that occupied 31.5% of the canal on average. Please review the document entitled: Web what are.
The nucleus is encased in a tougher, rubbery exterior, known as the annulus. The illustration in the upper left corner demonstrates a diffuse disc bulge. As a visual picture, the disc looks like a cream filled donut without a hole. What causes lumbar disk disease? Discs that become herniated usually are in an early stage of degeneration.
A herniated disk occurs when some of the nucleus pushes out through a tear in the annulus. Disc herniation can occur at different levels in the spine. Learn more about the options for treatment. In rare cases a large disc herniation can lead to cauda equina syndrome which requires emergent diagnosis and treatment. Understanding these stages is essential for treatment.
Web overall, 336 (91.3%) patients did not undergo surgery within 1 year of the ldh diagnosis. A herniated disk occurs when some of the nucleus pushes out through a tear in the annulus. Web lumbar disc herniation is a very common cause of low back pain and unilateral leg pain, known as radiculopathy. These discs function to give both support.
Web a lumbar disc herniation is a change in a spinal disc in the lower back, caused by degeneration or injury. A herniation may contain nucleus pulposus, vertebral endplate cartilage, apophyseal bone/ osteophyte and annulus fibrosus. Web to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of limited discectomy (ld) and aggressive discectomy (ad) performed via spinal endoscopy using the transforaminal approach.
The total canal area, and the area of the disc herniation. Web a spinal disk has a soft, jellylike center called a nucleus. The illustration in the upper left corner demonstrates a diffuse disc bulge. Web disc herniation refers to the displacement of intervertebral disc material beyond the normal confines of the disc but involving less than 25% of the.
Disc Herniation Size Chart - Web radiographic characteristics—including size of disc herniation (mm2), size of spinal canal (mm2), location of herniation on axial (central, paracentral, foraminal) and sagittal (disc level, suprapedicle, pedicle, infrapedicle) planes, and type of herniation (bulge, protrusion, extrusion, sequestration)—were measured by 2 independent, orthopedic. Lumbar disk disease is caused by a change in the structure of the normal disk. A herniated disk occurs when some of the nucleus pushes out through a tear in the annulus. Web lumbar disc herniation is a very common cause of low back pain and unilateral leg pain, known as radiculopathy. Discs that become herniated usually are in an early stage of degeneration. The treatment procedure and recovery time depend on the stage of the slipped disc. Web among the many differential diagnoses of lbp, degenerative disc disease and lumbar disc herniation (ldh) are the most common. 1 al qaraghli mi, de jesus o. Please review the document entitled: What causes lumbar disk disease?
Outline the treatment and management options available for cervical disc herniations. These discs function to give both support and flexibility to the spine. The intervertebral discs are the cushions that act as shock absorbers between each of the vertebra in your spine. Understanding these stages is essential for treatment and exercise. As a visual picture, the disc looks like a cream filled donut without a hole.
Web the onset of symptoms is usually sudden with no apparent cause but is sometimes triggered by movements or activities that place stress on the disc, such as lifting or twisting. Web a “disc herniation” is defined as a discal prominence that does not exceed 50% of the disc circumference. A slipped intervertebral disc passes through four stages. Learn more about the options for treatment.
Web this series was used to develop the msu classification as an objective measure of lumbar disc herniation on mri to define “substantial”. Understanding these stages is essential for treatment and exercise. What causes lumbar disk disease?
Web what are the 4 stages of disc herniation? Web a lumbar disc herniation is a change in a spinal disc in the lower back, caused by degeneration or injury. Understanding these stages is essential for treatment and exercise.
Web A Spinal Disk Has A Soft, Jellylike Center Called A Nucleus.
In rare cases a large disc herniation can lead to cauda equina syndrome which requires emergent diagnosis and treatment. Learn more about the options for treatment. The treatment procedure and recovery time depend on the stage of the slipped disc. For comparison purposes, please refer to figure 1.
Web A Lumbar Disc Herniation Is A Change In A Spinal Disc In The Lower Back, Caused By Degeneration Or Injury.
Web the onset of symptoms is usually sudden with no apparent cause but is sometimes triggered by movements or activities that place stress on the disc, such as lifting or twisting. Web among the many differential diagnoses of lbp, degenerative disc disease and lumbar disc herniation (ldh) are the most common. What causes lumbar disk disease? The intervertebral discs are the cushions that act as shock absorbers between each of the vertebra in your spine.
Web A Herniated Disc (Also Called Bulged, Slipped Or Ruptured) Is A Fragment Of The Disc Nucleus That Is Pushed Out Of The Annulus, Into The Spinal Canal Through A Tear Or Rupture In The Annulus.
To better understand how a herniated disc occurs, it is helpful to know some anatomy of the spine and more specifically, the parts of the spine involved. Web what are the 4 stages of disc herniation? Please review the document entitled: Web radiographic characteristics—including size of disc herniation (mm 2 ), size of spinal canal (mm 2 ), location of herniation on axial (central, paracentral, foraminal) and sagittal (disc level, suprapedicle, pedicle, infrapedicle) planes, and type of herniation (bulge, protrusion, extrusion, sequestration)—were measured by 2 independent, orthope.
As A Visual Picture, The Disc Looks Like A Cream Filled Donut Without A Hole.
Disc herniation can occur at different levels in the spine. The total canal area, and the area of the disc herniation. Understanding these stages is essential for treatment and exercise. A slipped intervertebral disc passes through four stages.